SSL Certificate Types


Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates
What is a Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificate?
A Domain Validation (DV) SSL certificate is one of the simplest and most common SSL certificates available. It’s designed to secure the connection between your website and visitors by encrypting the data. DV certificates confirm that the person requesting the certificate owns the domain they’re securing. This type of certificate is ideal for personal websites, blogs, and informational sites where the primary goal is to protect sensitive data like login credentials or form submissions.
When you apply for a DV SSL certificate, the Certificate Authority (CA) verifies your domain ownership by checking the domain’s registration information. It does not verify the identity of the individual or the organization behind the site, making it quicker and simpler to obtain than other SSL certificate types. DV certificates are perfect for sites that need encryption quickly without extensive validation.
How DV SSL Certificates Work
The process of obtaining and implementing a DV SSL certificate is straightforward:
- Apply for a DV Certificate: You should apply through a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). You must provide some basic details, such as your domain name.
- Domain Ownership Verification: The CA will email the domain’s registered contact (usually in the domain’s WHOIS records). This email contains a verification link to prove that you own the domain.
- Certificate Issuance: Once you click the verification link, the CA will approve and issue the certificate. Depending on the CA, this process typically takes just a few minutes.
- Install the SSL Certificate: Once issued, you can install the DV SSL certificate on your server. It ensures that all data exchanged between your site and visitors is encrypted.
The simplicity of this process makes DV certificates one of the quickest SSL solutions available.
Benefits of DV SSL Certificates
One of the key advantages of DV SSL certificates is how quickly they can be issued. Since they don’t require an in-depth verification process, you can have an SSL certificate on your website within minutes. Additionally, they are one of the most affordable options, making them attractive for smaller websites or personal blogs.
DV certificates also enhance your website’s security by encrypting data, which helps prevent hackers from intercepting sensitive information. While they don’t provide the same level of trust as other certificates, they still show visitors that your website is taking the necessary steps to protect their data.
Another benefit is that having an SSL certificate on your website, even a DV certificate, will remove the “Not Secure” warning that browsers like Chrome display for sites without SSL. It improves user experience and boosts trust, even for smaller sites.
Limitations of DV SSL Certificates
While DV SSL certificates offer solid encryption and some essential trust, they have a few limitations. The most significant drawback is that they only verify domain ownership and do not confirm the website owner’s identity. Visitors may not have the highest trust in your site, especially if you run an e-commerce store or handle sensitive transactions.
DV certificates do not offer the same level of security and credibility as higher validation certificates, such as Organization Validation (OV) or Extended Validation (EV). An EV or OV certificate would be a better option for sites where establishing user trust is critical, like financial services or online stores.
Additionally, while DV certificates are outstanding for encrypting data, they don’t offer advanced security features like enhanced organization validation or extended identity verification. If you need to give visitors greater confidence in your website’s legitimacy, a more robust SSL certificate may be required.
Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates
What is an Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificate?
An Organization Validation (OV) SSL certificate provides an extra layer of trust and security compared to a Domain Validation (DV) certificate. While DV certificates only verify domain ownership, OV certificates go a step further by confirming both the domain’s ownership and the legitimacy of the organization behind the website.
To get an OV certificate, the Certificate Authority (CA) will perform a more thorough vetting process, including verifying the organization’s legal existence. This involves checking government databases and company records and contacting the organization for confirmation. Once validated, an OV certificate encrypts the data on your site and ensures visitors can see that a verified organization operates your site. This makes OV certificates a trusted choice for businesses looking to establish credibility online.
How OV SSL Certificates Differ from DV Certificates
The primary difference between OV SSL and DV certificates lies in the validation process and the level of trust they provide to website visitors. DV certificates are quicker and easier to obtain because they only require domain ownership verification. This makes them an affordable option but doesn’t offer much assurance about the legitimacy of the website owner.
On the other hand, OV certificates require a more thorough verification process. The CA verifies the domain and checks the organization’s legal status. This added layer of validation increases the level of trust in your site. Visitors can be confident that a legitimate business or organization runs the site when they see an OV certificate.
OV certificates also display more detailed information on the site’s security features. For example, some browsers will show the organization’s name alongside the padlock symbol in the address bar, which is a clear indication that the site has undergone a more extensive vetting process.
Benefits of OV SSL Certificates
The key benefit of OV SSL certificates is their higher trust level than DV certificates. When visitors see that a trusted Certificate Authority has validated your site, they are more likely to feel secure when interacting with your website, especially if they are entering personal information like contact details or making a purchase.
Additionally, OV certificates provide more substantial security features than DV certificates. They ensure that all data exchanged between your website and visitors is encrypted, preventing hackers from intercepting sensitive information. This is especially important for businesses that handle customer information, like online retailers or service providers.
Another benefit is the enhanced credibility an OV certificate brings to your website. Visitors will notice the added security features and be more confident doing business with you. Whether you run an e-commerce store, a financial service, or a health-related site, having an OV certificate signals that your site is secure and trustworthy.
Who Should Use OV SSL Certificates?
OV SSL certificates are ideal for businesses, organizations, or any public-facing website where trust and credibility are essential. If you run an e-commerce site, provide financial services, or have a website where users share personal or sensitive information, an OV certificate will give visitors the confidence they need to interact with your site safely.
Non-profit organizations, educational institutions, and any other organization that wants to show visitors that they are a legitimate entity should also consider an OV certificate. The added verification helps ensure that your website is recognized as trustworthy, leading to higher engagement, more conversions, and a better overall user experience.
In short, an OV SSL certificate is the right choice if your site represents a business or organization and you want to give your visitors higher security and trust.
How Long Does it Take to Issue an OV SSL Certificate?
Obtaining an OV SSL certificate takes longer than a DV certificate due to the additional validation steps required. On average, the Certificate Authority can take 1 to 5 business days to verify your organization’s information and issue the certificate.
The time it takes may vary depending on the complexity of your organization’s verification process. For example, it could take longer if the CA needs additional documents or issues verifying your business details. However, once the organization is validated, the actual installation of the certificate on your website can be completed quickly, often within a few hours.
Keep in mind that the extended validation process is crucial for ensuring the security and credibility of your site. The additional time spent during the process will pay off in the trust and confidence it builds with your visitors.


Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates
What is an Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificate?
An Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificate is the highest level of SSL certification available. It gives your website the strongest encryption and security while offering users the most visible trust indicators. EV certificates encrypt the data exchanged between your site and visitors and involve a rigorous verification process that checks the legitimacy of the organization behind the website.
Unlike Domain Validation (DV) or Organization Validation (OV) certificates, which only verify domain ownership or the organization’s identity, EV certificates require a deeper level of validation. The Certificate Authority (CA) verifies the legal existence of the organization, its physical location, and operational status. Once verified, the website gets the highest trust from browsers and users. EV SSL certificates are usually chosen by large businesses, banks, and any website where security and user trust are critical.
How EV SSL Certificates Enhance Trust
One of the standout features of EV SSL certificates is the visual trust indicators they provide. Most browsers display a green address bar with the organization’s name when a website has an EV certificate. This indicator tells users the website is secure and has undergone thorough vetting. This green bar serves as a clear signal to visitors that the website they are on is not only safe but also verified by a trusted third party.
This visual cue is powerful because it instills immediate confidence. Users who see the green bar are likelier to trust the website, feel secure sharing personal or financial information, and continue browsing or making purchases. This level of trust can significantly improve conversion rates, customer engagement, and overall satisfaction.
Benefits of EV SSL Certificates
The benefits of EV SSL certificates extend beyond just encryption. Here’s why businesses choose EV certificates:
- Maximum Security: EV certificates provide top-notch encryption, ensuring that data transmitted between your website and visitors is protected against cyber threats.
- Visual Trust Indicators: As mentioned, the green address bar and the organization’s name in the browser address bar indicate trustworthiness. This feature is unique to EV certificates and unavailable with DV or OV certificates.
- Higher Consumer Confidence: EV certificates help build trust and credibility, particularly for websites where users share sensitive information, like online shopping or banking. The visual indicators and thorough validation reassure customers that the site they interact with is legitimate.
- SEO Boost: While there’s no direct ranking factor for EV certificates, having an EV certificate on your site can contribute to better user trust, indirectly boosting your site’s performance in search engine rankings.
- Legal Verification: With an EV SSL, visitors know that the business behind the website has been legally validated, which is especially important for industries involving financial transactions or privacy.
How to Obtain an EV SSL Certificate
Obtaining an EV SSL certificate requires a more in-depth process than other SSL certificates. Here’s how the process typically works:
- Choose a Certificate Authority (CA): The first step is to select a trusted CA from which you want to purchase the EV SSL certificate. It could be a provider like Symantec, Comodo, or DigiCert.
- Provide Documentation: To verify your business’s legitimacy, the CA will require a variety of documents, including:
- Proof of your organization’s legal existence (such as government-issued incorporation records).
- Physical location details.
- Verification of domain ownership.
- Legal proof of the entity’s right to use the domain.
- Certificate Authority Review: The CA will review the submitted documentation and perform an extensive background check on your organization. This process typically takes longer than other certificate types, ranging from 5 to 10 business days.
- Issuance of the Certificate: Once the validation process is complete and your organization passes the review, the CA will issue the EV SSL certificate. You can install it on your server, and your website will display the green address bar in compatible browsers.
Who Should Choose EV SSL Certificates?
EV SSL certificates are designed for businesses and websites where trust and security are paramount. These certificates are particularly beneficial for:
- Large Corporations: Companies with high traffic volumes or industries where security and trust are critical (e.g., finance, healthcare, and e-commerce) should opt for EV certificates.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and payment processing websites benefit significantly from EV certificates, as they need to instill confidence in users entering sensitive financial data.
- E-commerce Platforms: Online stores handling transactions and processing credit card information should use EV SSL certificates to ensure secure and trustworthy transactions.
- Government and Legal Websites: Government entities or websites dealing with legal matters need the highest trust and security, making EV certificates a perfect fit.
Wildcard SSL Certificates
What is a Wildcard SSL Certificate?
A Wildcard SSL Certificate is a unique security certificate used to protect your website and all its subdomains under a single certificate. This means that if you have multiple subdomains like shop.yourdomain.com, blog.yourdomain.com, or support.yourdomain.com, you don’t need a separate SSL certificate for each of them. Instead, one WildCard SSL certificate can secure all of them at once.
The purpose of a WildCard SSL certificate is simple—it provides a secure connection for visitors to your website by encrypting the data exchanged between your website and its users. This ensures that sensitive information, like login credentials or payment details, is protected from hackers and malicious actors. It’s beneficial for businesses with numerous subdomains that need to be secured, making it a convenient, cost-effective option to maintain trust and security online.
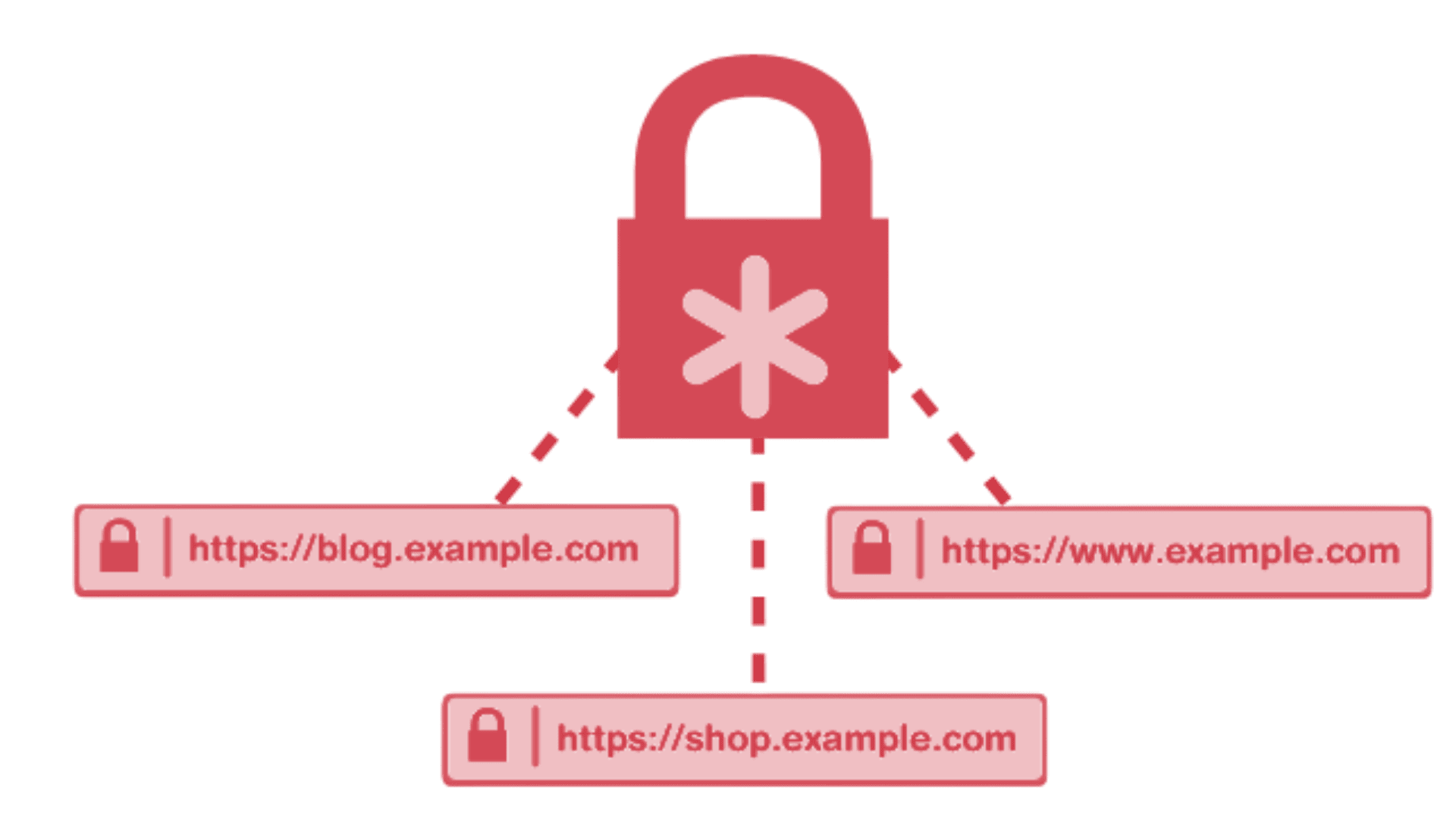
Encrypt unlimited subdomains with one wildcard certificate
How WildCard SSL Certificates Work
A WildCard SSL Certificate uses a wildcard symbol (*) before your domain name. This allows you to secure your main domain and all of its subdomains. For example, if you purchase a WildCard SSL for *.yourdomain.com, this will protect yourdomain.com, shop.yourdomain.com, blog.yourdomain.com, and any other subdomains you create in the future.
The wildcard acts as a placeholder for any subdomain, so you don’t have to buy a new certificate whenever you create a new subdomain. The WildCard SSL ensures that all the data transmitted across these subdomains is encrypted so users can browse confidently, knowing their data is secure.
Benefits of WildCard SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL Certificates come with several significant benefits that make them an attractive option for businesses:
- Cost-effective: Instead of purchasing individual SSL certificates for each subdomain, you only need one WildCard SSL. This can save you a lot of money, especially if you have many subdomains to secure.
- Simplified management: Managing one SSL certificate is much easier than keeping track of several. You only need to renew and install one certificate, which makes it less time-consuming and easier to keep your site secure.
- Flexible: Wildcard certificates allow you to create as many subdomains as you need without worrying about buying additional certificates. This is particularly useful for businesses that expand or change their structure over time.
- Enhanced security: Like any other SSL certificate, WildCard SSL ensures encryption and protects sensitive data. It enhances the overall security of your website by providing a strong layer of protection across multiple subdomains.
Limitations of WildCard SSL Certificates
While WildCard SSL Certificates offer a lot of benefits, they do come with some limitations:
- Not suitable for multiple domain names: Wildcard SSL certificates only secure a single domain and its subdomains. If you run multiple domains, each domain will need its own Wildcard SSL certificate or another type of SSL, such as a Multi-Domain SSL.
- Limited to one level of subdomains: Wildcard SSL certificates can only secure the immediate subdomains of your primary domain. For example, *.yourdomain.com will cover blog.yourdomain.com, but it won’t cover sub.blog.yourdomain.com. To secure deeper subdomains, you may have to look into other options.
- Security concerns for multi-level subdomains: If you run a complex structure of subdomains, some security experts suggest that Wildcard SSL certificates might not offer the same control or detailed security level as individual certificates for each subdomain.
Wildcard SSL Certificate vs. Multi-Domain SSL Certificate
WildCard SSL and Multi-Domain SSL Certificates are designed to secure multiple domains but cater to different needs.
- Wildcard SSL Certificate: This certificate secures your main domain and all its subdomains. It is the right option if you have a single domain with many subdomains. However, it only works for one domain and cannot secure multiple domains.
- Multi-Domain SSL Certificate: This certificate allows you to secure multiple domains with a single certificate. For instance, you can protect yourdomain.com, anotherdomain.com, and yetanotherdomain.com under one certificate. Unlike the WildCard SSL, Multi-Domain SSL does not cover subdomains but allows you to secure different domains within the same certificate.
The key difference here is that WildCard SSL is focused on securing subdomains under one domain. At the same time, Multi-Domain SSL allows you to secure multiple domains without the need for separate certificates. Depending on your business needs—whether you are managing one domain with many subdomains or multiple distinct domains—choosing the correct certificate is crucial for maintaining efficient security.

Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL Certificates
What is a Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL Certificate?
A Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificate is an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate designed to secure multiple domains and subdomains under one certificate. It combines two essential concepts: Subject Alternative Name (SAN) and Unified Communications Certificate (UCC).
Subject Alternative Name (SAN): SAN is an extension of the SSL certificate that allows it to cover multiple domain names within a single certificate. For instance, if your company owns example.com, example.net, and example.org, a SAN SSL certificate can secure all three domains.
Unified Communications Certificate (UCC): UCC was initially designed for securing Microsoft Exchange and Office Communications servers, but today, it’s used as a broader term for certificates that secure multiple domains and subdomains, making it suitable for businesses that need to ensure a variety of web services.
By combining both SAN and UCC, this certificate allows businesses to secure a range of domain names and subdomains without the hassle of managing multiple SSL certificates. This flexibility is perfect for organizations with many websites or services that need encryption.
How Multi-Domain SAN/UCC Certificates Work
Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificates allow you to secure several domains and subdomains with just one certificate. For example, if you have different websites like yourcompany.com, yourcompany.net, and yourcompany.org, you can add them all as SAN entries to a single UCC SSL certificate. This is particularly useful for businesses with multiple websites or services, as it provides a simple and centralized way to manage SSL encryption.
A Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificate can secure multiple top-level domains and subdomains, such as blog.yourcompany.com, shop.yourcompany.com, or support.yourcompany.net. The certificate is a universal solution that enables you to safeguard a diverse array of web services, simplifying management and minimizing expenses.
Benefits of Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL Certificates
There are several key benefits to using Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificates, especially for businesses with many domains and subdomains:
- Versatility: Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificates allow you to secure multiple domains and subdomains, giving you flexibility without buying separate certificates. Whether you’re managing several brands or a range of services, a Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificate can meet all your needs.
- Cost-efficiency: Purchasing multiple individual SSL certificates can quickly become expensive, especially for businesses with many domains. A Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificate consolidates this cost into one affordable option, helping companies to save money in the long run.
- Easy management: Managing a single SSL certificate for all domains is far simpler than dealing with multiple certificates. You’ll only need to renew and install one certificate, which reduces administrative work and the chances of errors.
- Improved security: Like any other SSL certificate, Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificates provide strong encryption to secure the data transferred between your website and its visitors. It ensures that sensitive information, like customer or transaction details, is protected.
Who Should Use Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL Certificates?
Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificates are ideal for businesses with multiple domains or subdomains, especially if these domains are part of different services or departments. If you’re running several websites or platforms, such as a main website, a blog, an online store, and a customer service portal, a Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificate can simplify your SSL management by covering them all under one certificate.
For example, if you have multiple geographic locations with different domains, like us.yourcompany.com and eu.yourcompany.com, a Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificate can secure both domains in one go. It’s also an excellent option for businesses with many subdomains that need encryption, as it can cover all those under a single certificate.
Ultimately, Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificates are designed for companies that want to streamline their security efforts while saving money and reducing management complexity.
Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL vs Wildcard SSL Certificates
Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificates and Wildcard SSL certificates are used to secure multiple domains, but they serve slightly different purposes and are suitable for various use cases.
- Wildcard SSL Certificate: A Wildcard SSL is designed to secure a domain and its subdomains. For example, if you secure *.yourcompany.com, it will cover www.yourcompany.com, blog.yourcompany.com, and any other subdomains of yourcompany.com. However, Wildcard SSL certificates can only cover one domain (e.g., yourcompany.com), and they don’t secure entirely different domains (e.g., yourcompany.net).
- Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL Certificate: A Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL certificate is more flexible and can secure multiple top-level domains and subdomains. For example, a Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificate can secure yourcompany.com, yourcompany.net, and yourcompany.org, along with subdomains like shop.yourcompany.com and blog.yourcompany.net. This makes Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificates great for businesses managing websites or services.
Key Differences:
- Wildcard SSL: Best for a single domain and its subdomains.
- Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL: Ideal for multiple domains and subdomains, offering broader coverage.
When deciding between the two, consider whether you need to secure multiple domains or subdomains. If you want to protect different domains, Multi-Domain SAN/UCC certificates are the better choice, while Wildcard SSL certificates are perfect for managing a single domain with multiple subdomains.
Code Signing Certificates
What is a code signing certificate?
A Code Signing Certificate is a digital certificate that software developers use to sign their applications, ensuring that the code remains secure and has not been tampered with. When you download software from the internet, there’s always a risk that it might be altered or compromised by hackers. A code signing certificate helps to prevent this by providing a secure digital signature that proves the software is authentic and has not been altered since it was signed.
This certificate functions as a “certificate of approval” from the software developer. When you run an application signed with a Code Signing Certificate, your computer verifies the signature to ensure it matches the original version of the software. If any changes have been made, the signature will no longer be valid, warning users that the software might not be trustworthy. For developers, using a Code Signing Certificate ensures that their software is delivered securely and maintains the integrity of the code. It’s essential for protecting the developer’s reputation and the users’ trust.
How Code Signing Certificates Protect Software
Code signing certificates protect software from tampering and ensure that the software you download is legitimate. When you sign your software with a Code Signing Certificate, you’re essentially “locking” the code in a way that makes it tamper-proof. Any modification to the code will break the digital signature, signaling to users and their devices that the software may have been compromised. In addition to preventing tampering, Code Signing Certificates also provide a way to verify the authenticity of the software. The certificate contains information about the publisher so users can confirm that the software came from a trusted source. It helps prevent malware, trojans, or viruses from disguising themselves as legitimate applications. Software developers use Code Signing Certificates to ensure that their programs are delivered safely and securely to users. It maintains the integrity of the software and gives users confidence that they are installing a trusted product.
Benefits of Code Signing Certificates
Using a code signing certificate offers several significant benefits for both developers and users:
- Boosts Trust in Software: When users see a program signed with a valid certificate, they are more likely to trust it. The digital signature assures them that the software hasn’t been altered by anyone other than the developer.
- Increases User Confidence: Many security software programs, including antivirus and firewall systems, check for a valid code signature. If the software is signed, it’s less likely to be flagged as a security risk. It leads to fewer security warnings and increased confidence in your software.
- Reduces Security Warnings: Unsigned software often triggers notifications or alerts from operating systems like Windows or macOS, telling users that the software may be risky or unknown. With a Code Signing Certificate, you can avoid these warnings, making it easier for users to install and run your software without interruptions.
- Prevents Malware and Tampering: The primary function of a Code Signing Certificate is to protect your software from tampering. It ensures that users install the exact program version the developer intended, free from malicious alterations.
Requirements for Obtaining a Code Signing Certificate
To obtain a Code Signing Certificate, you must undergo a validation process to prove your identity and legitimacy as a software publisher. Here are the general steps involved:
- Choose a Certificate Authority (CA): The first step is to choose a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), such as DigiCert, GlobalSign, or Comodo, that issues Code Signing Certificates.
- Submit Documentation: You will be required to submit documentation to verify your identity and your business. It typically includes a government-issued ID, business registration information, and other details that prove you are a legitimate software developer or publisher.
- Generate a Key Pair: Once your identity is verified, you’ll generate a public and private key pair. The private key is used to sign your software, while the public key is included in the certificate to verify the signature.
- Certificate Issuance: After you submit the required documents and complete the validation process, the CA will issue your Code Signing Certificate. You can then use it to sign your software.
- Use the Certificate to Sign Software: Once you have the certificate, you can start signing your software. It can typically be done using tools provided by the CA or through your development environment.
Obtaining a code signing certificate requires effort and documentation, but it’s well worth the effort to ensure that users trust your software and that it is protected against tampering.
Code Signing vs. SSL Certificates
While both Code Signing Certificates and SSL Certificates play essential roles in securing online interactions, they serve different purposes:
- Code signing certificates are focused on securing the software itself. They ensure that the distributed software hasn’t been tampered with and is from a trusted source. Code signing certificates protect the integrity of the code and prevent malicious actors from altering the software before it reaches the user.
- On the other hand, SSL certificates secure data transmitted over the internet between a web server and a browser. During online transactions, they encrypt the data to prevent hackers from intercepting sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card details.
Key Differences:
- Code Signing Certificates: Secure software applications and verify the authenticity of code.
- SSL Certificates: Secure online communication and protect user data transmitted between websites and visitors.
While both certificates focus on security, Code Signing Certificates are specifically for software development, while SSL Certificates are used for protecting websites and online data. If you’re a software developer, a Code Signing Certificate is essential to ensure your applications are trusted and secure. SSL certificates are vital for any website that handles sensitive user information.

Flex SSL Certificates
What is a Flex SSL Certificate?
A Flex SSL Certificate is a unique SSL certificate designed to offer flexible security options for websites, particularly those operating in dynamic or evolving server environments. Unlike traditional SSL certificates, which are usually tied to specific hosting environments or configurations, Flex SSL certificates are adaptable and can be used in various scenarios.
Flex SSL certificates are especially useful for businesses that require a more scalable and versatile security solution. They allow website owners to secure their sites without worrying about whether they are on shared hosting, dedicated servers, or cloud environments. This adaptability makes them a go-to option for websites that frequently change or update their infrastructure.
Flexibility of Flex SSL Certificates
One of the standout features of Flex SSL certificates is their remarkable flexibility. These certificates can easily be used across various hosting environments, whether your site is on shared hosting, dedicated hosting, or a cloud-based server. This makes them a perfect solution for businesses that may change their hosting setup over time or need a solution that can simultaneously work with multiple hosting types.
In a shared hosting environment, multiple websites share the same server, but Flex SSL certificates can still provide security to each site without causing conflicts. Similarly, Flex SSL certificates ensure that the encryption and data security standards are maintained for websites hosted on dedicated servers or cloud platforms, regardless of the hosting configuration. This means you won’t have to worry about finding a new SSL certificate whenever you change or upgrade your hosting setup.
Benefits of Flex SSL Certificates
Flex SSL certificates offer several key benefits, making them an excellent choice for businesses that prioritize security and adaptability:
- Enhanced Flexibility: As the name suggests, Flex SSL certificates are highly flexible. They can seamlessly transition between different hosting environments, making them a reliable option for businesses that frequently change their server configurations.
- Support for Multiple Hosting Types: Whether you’re using shared hosting, a dedicated server, or a cloud service, Flex SSL certificates provide robust encryption across all these platforms. This eliminates the need to purchase different SSL certificates for different hosting setups.
- Improved Security: Like other SSL certificates, Flex SSL ensures that your website’s data is encrypted, protecting it from interception or tampering. Regardless of your hosting configuration, your website will benefit from secure, encrypted communication, helping to build trust with users and protect sensitive data.
- Scalability: Flex SSL certificates grow with your website. As your business scales and your hosting needs evolve, these certificates can adapt to secure your growing infrastructure without requiring frequent upgrades or changes.
Use Cases for Flex SSL Certificates
Flex SSL certificates are particularly well-suited for websites with dynamic server environments or frequent changes in hosting configurations. Here are a few ideal use cases:
- E-commerce Websites: Many e-commerce sites experience fluctuating traffic and sometimes need to scale their hosting environments to accommodate peaks. Flex SSL certificates ensure that your website remains secure no matter where it is hosted—whether shared hosting during low traffic or a dedicated server during busy seasons.
- Startups and Growing Businesses: Small businesses and startups often begin with shared hosting but may upgrade to dedicated servers or cloud-based infrastructure as they grow. A Flex SSL certificate offers the scalability needed to secure a website through each transition without the hassle of constantly changing or upgrading the certificate.
- Websites with Multiple Subdomains: If you manage a website with multiple subdomains (e.g., blog.yoursite.com, shop.yoursite.com), Flex SSL can be applied across all these areas, regardless of how your server or hosting setup changes over time.
- Businesses with Changing Hosting Providers: Companies that frequently switch between hosting providers due to cost or performance considerations can rely on Flex SSL certificates to ensure their sites remain secure.
Flex SSL vs Traditional SSL Certificates
When comparing Flex SSL certificates with traditional SSL certificates, the key difference lies in scalability and versatility:
- Flex SSL Certificates: These certificates offer flexibility across various hosting environments. They are designed to work seamlessly with shared, dedicated, and cloud-based hosting services, making them highly adaptable to changing business needs and hosting configurations. Businesses needing a solution that can evolve with their growth will find Flex SSL certificates an ideal choice.
- Traditional SSL Certificates: These certificates are typically fixed to a specific type of hosting, meaning you might need to get a different certificate if you switch your hosting provider or infrastructure. Traditional SSL certificates are more limited in their flexibility, especially when it comes to websites that operate in dynamic or frequently changing environments.
If your website’s infrastructure is stable and unlikely to change often, a traditional SSL certificate could be a sufficient choice. However, if your site requires more flexibility, adaptability, and scalability, a Flex SSL certificate ensures ongoing security regardless of your hosting setup.
Document Signing Certificates
What is a Document Signing Certificate?
A Document Signing Certificate is a digital certificate used to authenticate the signer’s identity and ensure the integrity of a document. This certificate allows individuals or organizations to digitally sign documents, providing a secure way to prove that the document wasn’t tampered with after it was signed.
In the past, signatures on paper documents were the primary means of verifying authenticity. Today, a Document Signing Certificate offers a more secure and efficient way to do the same thing digitally. By applying a digital signature, you confirm that the signer is who they say they are and ensure that the document’s content remains unchanged after signing. This is especially important in sensitive industries where the integrity and authenticity of a document are critical, like in legal contracts, business agreements, and financial transactions.

How Document Signing Certificates Work
Document Signing Certificates work through digital signing, which involves using cryptographic techniques to secure the content of a document. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- Generate a Digital Signature: The signer creates a digital signature using their private key, part of the Document Signing Certificate. This private key is securely stored and only accessible to the signer.
- Attach the signature to the document: Once the document is signed, the signature is added to the file. This digital signature contains information that uniquely identifies the signer, such as their name and organization, along with a timestamp.
- Verify the Signature: Anyone who receives the signed document can verify its authenticity. They use the public key associated with the signer’s certificate to ensure the signature matches the document’s content. If the document’s content has been altered in any way after it was signed, the signature becomes invalid.
This process ensures that the document is both authentic and intact, making it easy for all parties involved to trust the validity of the signed document without the need for physical signatures.
Benefits of Document Signing Certificates
Document Signing Certificates come with several benefits that make them essential for businesses, governments, and legal entities:
- Secure: The digital signature ensures the security of documents by preventing unauthorized changes. If anyone attempts to alter a signed document, the signature becomes invalid, alerting the parties involved to potential tampering.
- Legally Binding: Digital signatures are recognized as legally binding in many countries, making them a valid form of signing contracts, agreements, and other essential documents. This eliminates the need for paper-based signatures and speeds up the finalization of significant contracts.
- Reduced Fraud: Since the digital signature is tied to the signer’s identity and cryptographically secure, it significantly reduces the risk of fraud. It’s difficult for someone to forge a valid digital signature, making it more secure than traditional signatures.
- Increased Trust: Using a Document Signing Certificate demonstrates a commitment to security and authenticity. This increases trust with clients, customers, and partners, as they can quickly verify the integrity and legitimacy of the document.
- Efficiency: Digital signatures streamline the process of signing and sharing documents. They remove the need for physical meetings and paperwork, making the document signing process faster and more efficient.
Who Uses Document Signing Certificates?
Document Signing Certificates are widely used in several sectors where the security and authenticity of documents are essential. Some of the ordinary users include:
- Legal Firms and Lawyers: Legal professionals use Document Signing Certificates to sign contracts, agreements, and court documents securely. Digital signatures are legally recognized, ensuring that the documents hold up in court.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and financial institutions use these certificates to securely sign loan agreements, financial statements, and other sensitive documents. This helps prevent fraud and ensures that all parties involved can trust the authenticity of the signed documents.
- Government Agencies: Many agencies require digital signatures for official documents, such as tax filings, permits, and licenses. Document Signing Certificates help streamline these processes and ensure that documents are authentic and secure.
- Businesses: Organizations of all sizes use Document Signing Certificates to sign employee contracts, non-disclosure agreements, and other business-related documents. This helps them maintain security and compliance with industry standards.
- Healthcare Providers: Healthcare organizations also benefit from these certificates when signing medical records, consent forms, and insurance documents, ensuring the privacy and integrity of sensitive patient information.
Document Signing vs Code Signing
While both Document Signing Certificates and Code Signing Certificates are used for security purposes, they serve different functions and protect different types of information:
- Document Signing Certificates: These certificates are used to sign and secure documents, ensuring the content remains unchanged and the signer’s identity is verified. They are typically used for contracts, agreements, legal documents, and other paperwork. The focus is on the authenticity and integrity of the documents.
- Code Signing Certificates: Software developers use code signing certificates to sign their software, ensuring that the code is from a trusted source and hasn’t been tampered with. Code signing certificates protect the software by giving users confidence that the application is safe to download and install without any risk of malicious code or alterations.
Key Differences:
- Scope: Document Signing Certificates secure documents, while Code Signing Certificates secure software applications.
- Use Case: Document Signing is typically used in legal, financial, and business contexts, while Code Signing is used primarily in the tech industry to secure software and applications.
While both types of certificates ensure security and trust, they apply to different types of content. Document-signing certificates secure documents, whereas code-signing certificates ensure the integrity of software code.
Choose the Right SSL Certificate for Your Website’s Security Needs
Whether you’re looking for basic security or advanced validation, we have the perfect solution. Explore our SSL certificate options and secure your site with confidence today!
Tailored SSL Solutions for Every Level of Security – Protect Your Website with Confidence!
Frequently Asked Questions About SSL Certificate Types
What is a Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificate?
What is an Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificate?
What is an Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificate?
What is a Wildcard SSL Certificate?
What are Multi-Domain SAN/UCC SSL Certificates?
What is a Code Signing Certificate?
What is a Flex SSL Certificate?
What is a Document Signing Certificate?
Why Do I Need an SSL Certificate?
Can I Get an SSL Certificate for Free?
How Do I Install an SSL Certificate?
Installing an SSL certificate involves several steps:
- Obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted provider.
- Install the certificate on your web server.
- Configure your website to use HTTPS, which involves updating your website’s settings to redirect traffic from HTTP to HTTPS.
- Test the SSL certificate to ensure it’s installed and working correctly. Many hosting providers offer tutorials to help you through the installation process, or you can get help from a professional.
How Long Does It Take to Get an SSL Certificate?
What is the Difference Between HTTPS and SSL?
Can I Use the Same SSL Certificate for Multiple Domains?
How Do SSL Certificates Improve SEO?
Search engines, particularly Google, prefer websites that use SSL certificates. Sites with HTTPS are ranked higher than those without because HTTPS is seen as a sign of a secure and trustworthy website. Implementing SSL can improve your site’s search engine ranking and protect your users’ data, which is increasingly important to search engines.
Are SSL Certificates Required for All Websites?
While not legally required for all websites, SSL certificates are essential for any site that handles sensitive information, such as e-commerce sites, login pages, or payment gateways. Without SSL, browsers will flag your site as “Not Secure,” which can deter visitors from using your site. Google also prioritizes HTTPS websites in its search rankings, making it a good practice for any business website.
